Building Physics - Design Guidelines
Effective building design requires a focus on reducing heat losses, optimising solar gains, and managing internal loads. This article provides practical guidelines for improving energy efficiency and comfort through thoughtful design and application of building physics principles.
Solar Absorption and Heat on Surfaces
Building surfaces are constantly exposed to the elements, absorbing and emitting heat throughout the day. This article explains how surface colour, material choice, and environmental conditions impact solar absorption and heat retention, helping you select the best materials for energy-efficient and durable construction.
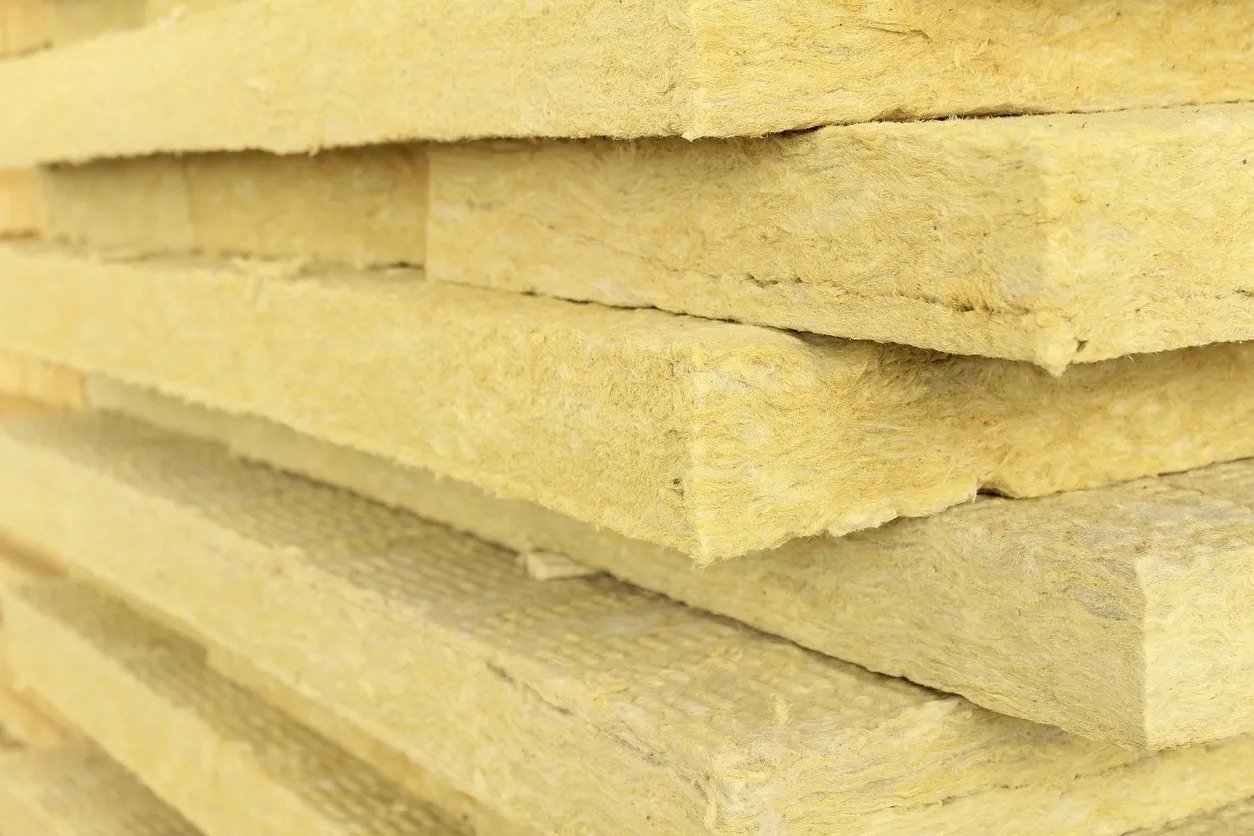
Insulation Properties and Application
Insulation plays a vital role in energy-efficient construction. Learn about the thermal conductivity, R-value, and the importance of moisture management in insulation performance. Discover the benefits of external vs. internal insulation systems and how to select the right material for your building.
Building Physics and Climate
Climate significantly affects building performance, influencing energy efficiency, material durability, and comfort. Learn how temperature, humidity, wind, and solar radiation shape building design and discover strategies for adapting to climate variations in construction.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how effectively building materials conduct heat. This article explains the significance of thermal conductivity (λ), its measurement using standards like ISO 8301 and ASTM C518, and how moisture can affect insulation performance. Understanding these factors is essential for energy-efficient building design.
Ventilation Basics
Proper ventilation is vital for maintaining indoor air quality and controlling moisture levels in buildings. Learn how air exchange rates, combined with mechanical ventilation systems, can prevent mold growth, manage pollutants, and improve comfort in your home.
Navigating Water Vapour Diffusion in Building Materials
Moisture management in buildings requires a deep understanding of the sd-value and MNs/g. These metrics help determine how materials resist and transmit water vapor, which is crucial in preventing condensation and structural issues. Learn how these values can guide better material choices for long-lasting, healthy buildings.
Relative Humidity, Condensate and Building Materials
Relative humidity and temperature play a key role in building moisture management. Condensation forms when warm, humid air meets cold surfaces, leading to issues like mold growth and structural damage. Learn how to control condensation through proper insulation, ventilation, and humidity management to create healthier, more durable buildings.
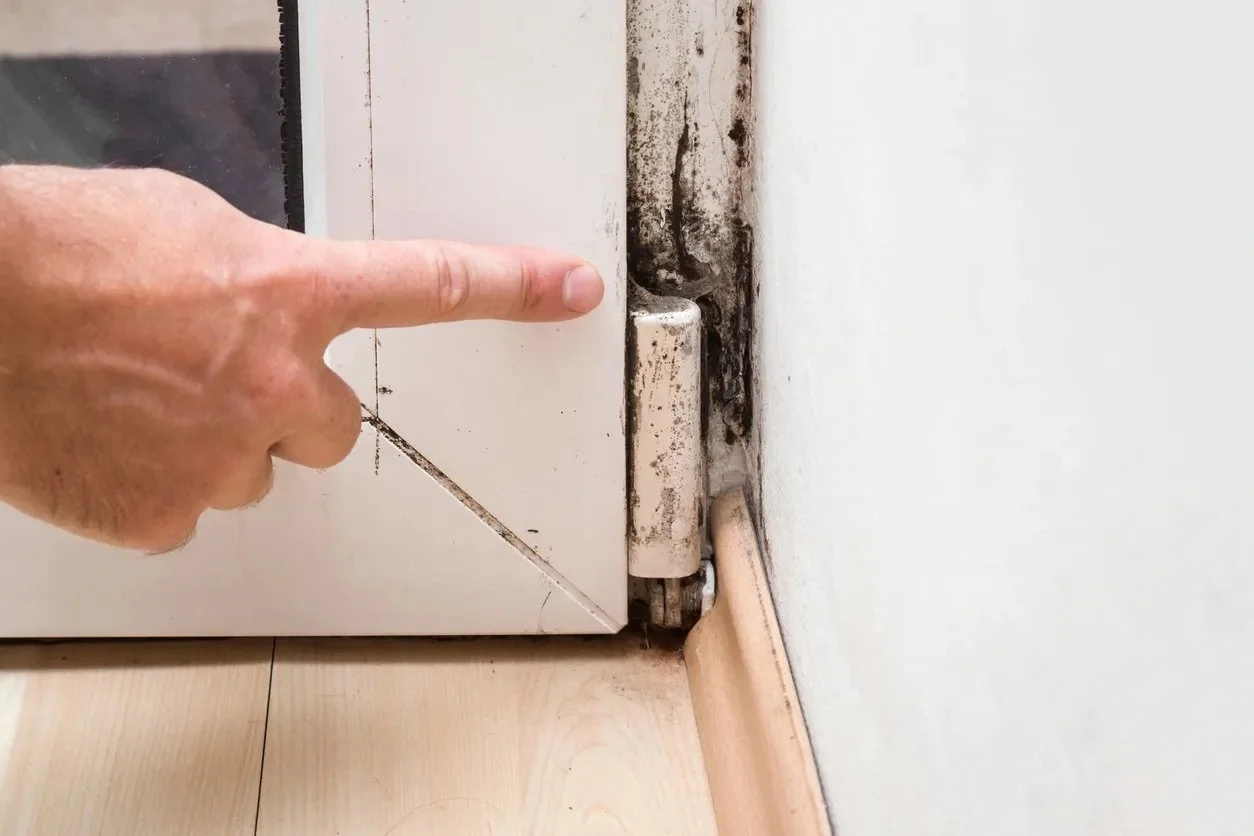
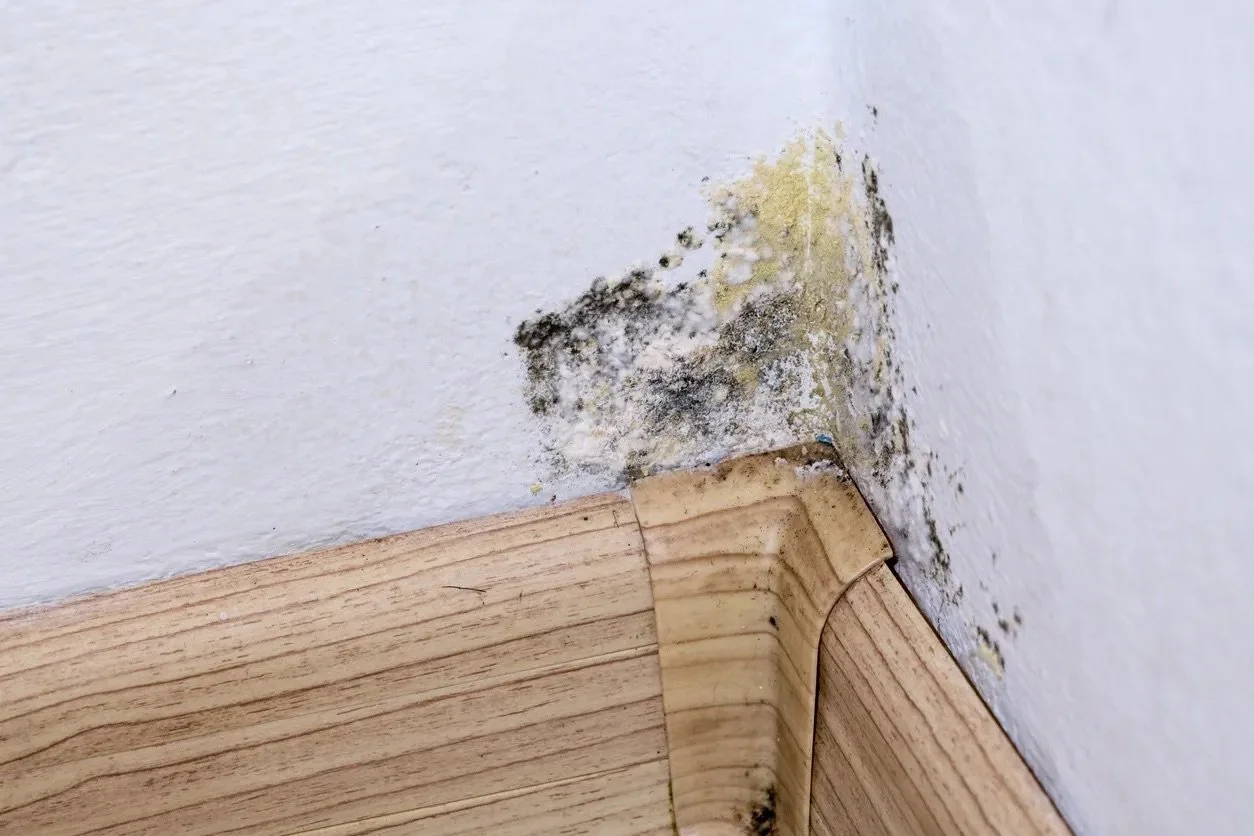
Condensation, mould and your health
Neglecting heating in your home can invite mould, which poses serious health risks over time. Exposure to mould spores can lead to allergies, asthma, and other respiratory issues. Learn when it's safe to handle mould removal on your own and when it's best to call in the experts.
Water Content in Construction Timber
Moisture content in construction timber is a critical factor that influences structural integrity and longevity. Excess moisture can lead to mold, decay, and even misdiagnosed condensation issues. Learn how to manage timber moisture effectively through proper storage, ventilation, and monitoring to prevent costly damage and ensure your building’s durability.
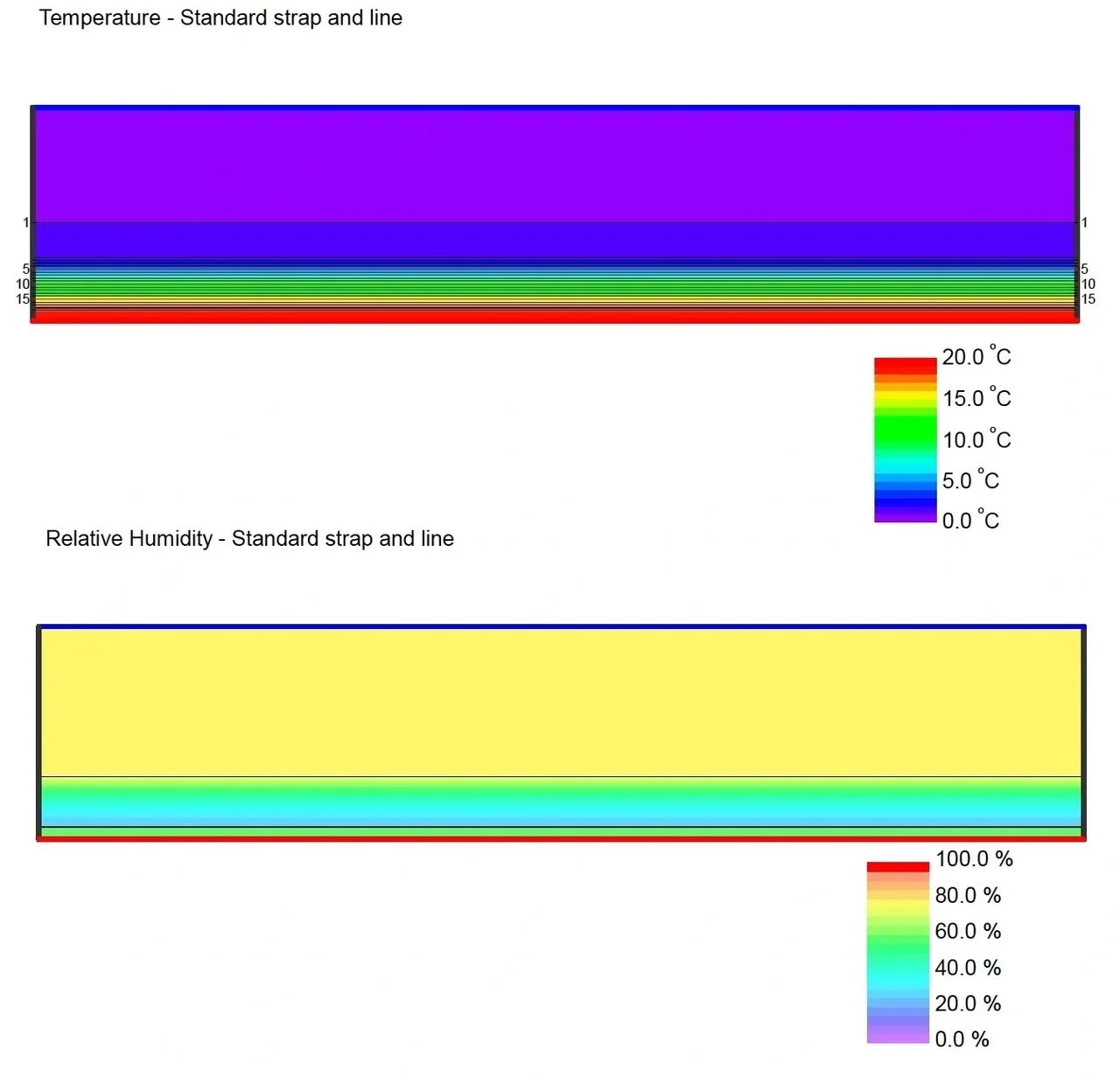
Strap and Line - Interior Insulation
Enhancing thermal insulation for historic facades while preserving aesthetics requires careful planning. Discover how interior insulation, vapour barriers, and hydrophobisation can protect both historical and modern structures from condensation, mould, and thermal bridges. Ensure long-lasting energy efficiency with the right materials and methods.
A Guide to ROI in “sustainable” Home Upgrades
Sustainable building upgrades offer more than just energy savings—they can significantly enhance your property’s value and long-term profitability. By investing in airtightness, insulation, and energy-efficient technologies, homeowners in New Zealand can enjoy reduced energy costs and higher property values. Learn how to maximize ROI with sustainable investments today.
IGU - Insulated Glass Unit
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) are essential in modern energy-efficient building design. With advanced low-emissivity coatings, IGUs reduce heat loss while maintaining high transparency, ensuring buildings remain energy-efficient and comfortable. Discover how integrating IGUs with sun protection glazing can prevent overheating and improve sustainability in architectural projects.
G-Value - Sun Protection in Glass
Sun protection glass, with its advanced Low-E coatings, is a key technology in reducing solar heat gain while allowing natural light to enter buildings. This innovation enhances energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and sustainability in modern architecture, making it essential for projects aiming to balance aesthetics and environmental responsibility.
Insulating with Glass
Advanced Glass Insulation: Enhancing Energy Efficiency in Modern Buildings
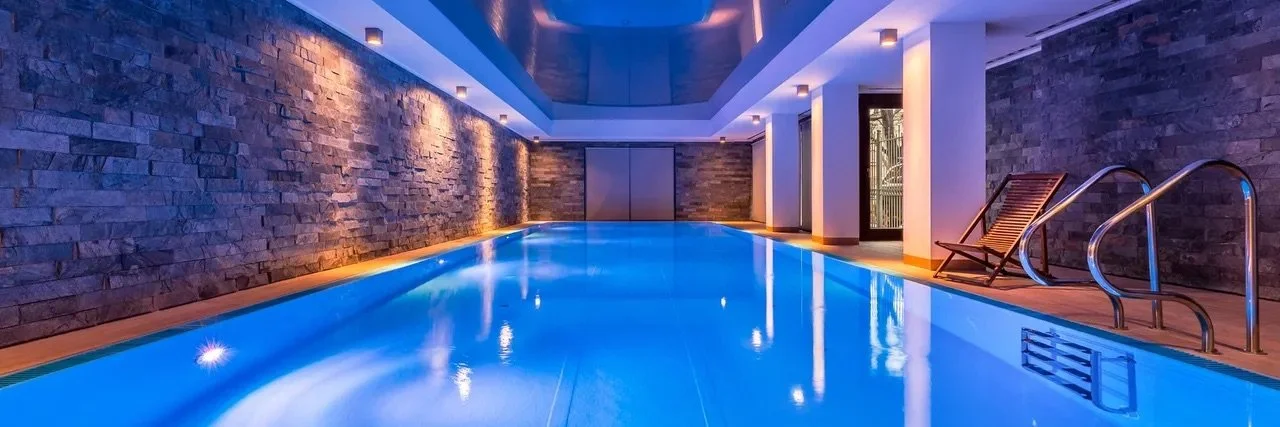
Building a successful Indoor Swimming Pool
Swimming pools present unique design challenges, including managing humidity, condensation, and energy efficiency. By understanding these conditions and selecting the right materials and systems, building professionals can create sustainable pools that stand the test of time. Embrace the principles of building physics to ensure your pool remains an enjoyable and efficient investment for years to come.
Condensation on Thermal Insulation Glass - exterior
Condensation on insulating glass windows is often seen as a flaw, but it's actually a sign of high-quality insulation. This natural occurrence shows that the glass is effectively reducing heat loss, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability. Embrace condensation as a mark of superior insulation and explore innovative solutions like self-cleaning coatings to manage moisture build-up.
Heat Transfer of Glass
In the realm of sustainable building design, glass is no longer a thermal weak point. Thanks to innovations like multi-pane insulating glass, noble gases, and Low-E coatings, glass now plays a crucial role in energy efficiency. These technologies reduce heat transfer, lower energy costs, and enhance building sustainability, proving that glass is essential to modern, eco-friendly design.
The Significance of Mould in Buildings
Mould in buildings is more than just an eyesore—it’s a signal of underlying issues in building design and performance. While the health impacts of mould, particularly in relation to asthma, remain debated, mould growth is a clear sign of moisture problems, poor ventilation, and insufficient heating. Recent studies, including those discussed in The Skeptics' Guide and Unbiased Science Podcast, indicate that while mould can exacerbate allergies and respiratory conditions, its direct link to more severe health outcomes may be overstated. Nevertheless, eliminating mould is crucial for both building integrity and occupant comfort. Addressing mould is not just about surface treatment—it requires improving the building’s insulation, ventilation, and overall energy efficiency.
Decarbonising Buildings Part 3: Policy and Regulation
In part 3 of our series on decarbonisation, we explore the critical role of policy and regulation in promoting sustainable construction and building operations. Policy frameworks are instrumental in driving the adoption of low-carbon materials, renewable energy, and energy-efficient designs, helping to reduce the building sector's carbon footprint. While carbon metrics serve as essential tools for setting and tracking decarbonisation goals, they should be integrated into a broader approach that values occupant health, resource efficiency, and long-term sustainability. Policies that balance carbon reduction with a holistic view of building health are key to fostering a sustainable future.